Is public Wi-Fi safe to use?

Posted on October 1, 2020 by Louise Howland
In 2019, 79% of UK adults owned a smartphone and it is safe to assume this number will only go up over time. People have become accustomed to being ‘connected’ all the time and increasingly wherever you go there seems to be public Wi-Fi that you can join to allow you to be online. But the question is should we be connecting to it? Customers often ask us how to use public Wi-Fi safely, in this blog we answer that question and explain what you need to consider before connecting and how to keep your data and devices secure when going online.
What is public Wi-Fi?
Public Wi-Fi is now available almost everywhere you go, most public places like airports, coffee shops, hotels, shops etc offer customers free access to the internet. Many people connect to these ‘hotspots’ without thinking and then browse the internet freely. Regardless of how legitimate these hotspots might appear, connecting to public Wi-Fi is a big security risk and should be avoided at all costs.
Is it safe to connect?
The short answer to this is NO. One of the reason for this is due to a scam which the cybersecurity industry refer to as the ‘Starbucks scam’ (although it has nothing to do with Starbucks specifically and relates to any public Wi-Fi) but following the coffee shop thread, the way the scam works is a person goes into the coffee shop and searches for a Wi-Fi point to connect to, at the top of the list is ‘Starbucks Free Wi-Fi.’ This may seem legitimate but in fact ‘Starbucks Free Wi-Fi’ is actually a hacker sat in the corner of the coffee shop with a laptop broadcasting a wireless access point. And if the person connects their mobile device to that Wi-Fi point, the hacker is then able to access your device and perhaps install software on your device, gaining access to your passwords and personal data.
In addition, hackers use unsecure Wi-Fi’s to distribute malware and place infected software on devices without the user realising they have been compromised. Another danger is public Wi-Fi is often an open connection which is unencrypted and unsecured, giving hackers the opportunity to exploit security flaws in the network to intercept data (this is often referred to as a Man in the Middle – MITM attack). Giving the hacker access to any information that passes between you and the websites you visit — including sensitive information, such as passwords and financial data.
Ensure your IT is at its strongest
Take back control with ramsac’s free self-assessment tool that helps to strengthen your business’ IT systems.

How can I use the internet safely when I am in public?
The safest way to use the internet when in you are in public places is to use the data tariff on your phone (4G or 5G), and if you are on a tablet or laptop, you can create a private hotspot on your phone and then tether your device to your mobile. To add an extra layer of protection you can connect through a VPN, although this adds extra privacy not necessarily additional security.
How to create a hotspot on your mobile device
For iPhone users
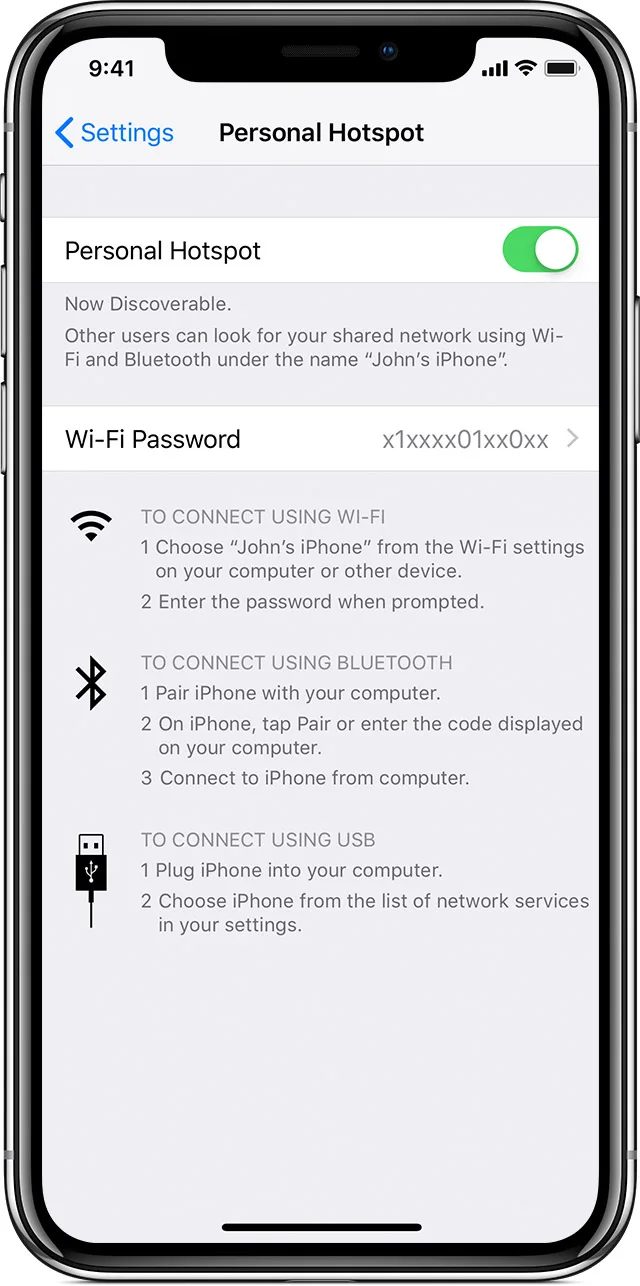
Go to Settings > Mobile Data or Settings > Personal Hotspot and tap the slider next to Allow Others to Join. When you connect a device to your Personal Hotspot, the status bar turns blue and shows how many devices have joined. The number of devices that can join your Personal Hotspot at one time depends on your network provider and iPhone model. If other devices have joined your Personal Hotspot using Wi-Fi, you can only use mobile data to connect to the Internet from the host device. You can connect using Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and USB and any devices wanting to join will need to enter the Wi-Fi password.
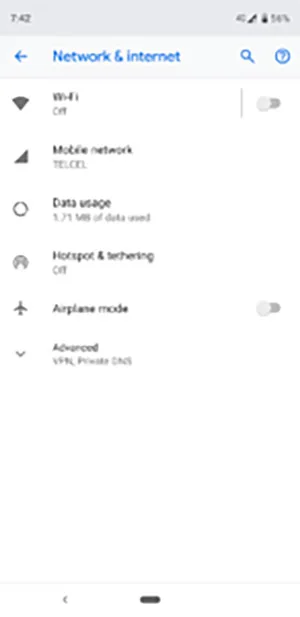
For Android users
- Open the Settings app;
- Tap the Network & internet option;
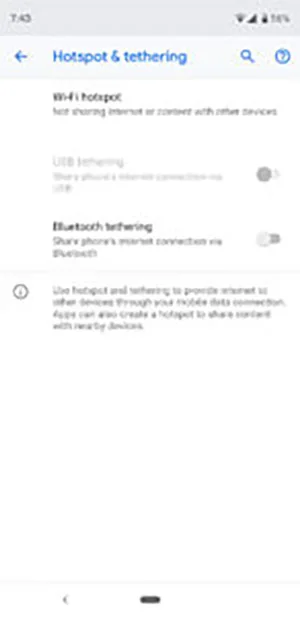
- Select Hotspot & tethering;
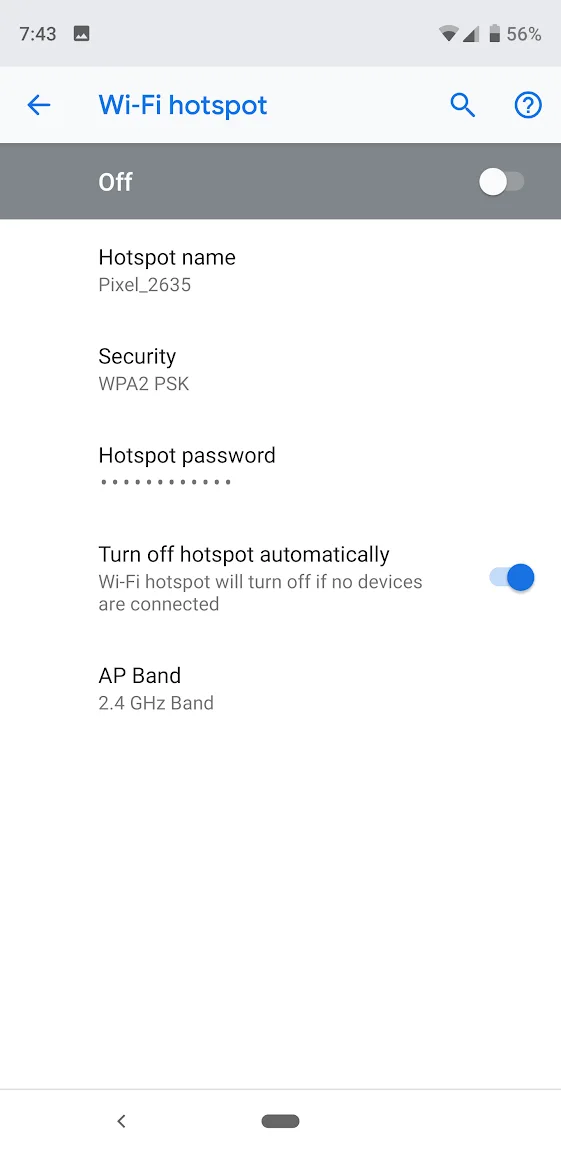
- Tap on Wi-Fi hotspot;
- This page has options for turning the hotspot feature on and off. Additionally, you can change the network name, security type, password, and more;
What is a Virtual Private Network?
A VPN is a virtual private network, this is a service that encrypts internet traffic to and from your device to prevent people from seeing what you are doing online or interfering with your device.
When you connect to a VPN service, it creates an encrypted “tunnel” over the internet. That secures the data traveling between you and your destination to protect your online identity. This can be anything from accessing to search engine to reading emails or doing online banking.
When you use VPN software, your device connects to the VPN provider’s servers. Your internet traffic passes through the VPN’s internet connection, meaning your private information is cloaked from your ISP and websites so they can’t log your web browsing and hackers can’t access your device. However, whilst VPN’s protect the privacy of the data you are transmitting it is important to understand that this VPN is a tunnel and therefore if there is an unsecure or infected device at either end of the tunnel, a VPN can allow an cyber infection to pass between the two endpoints.







