How to know if a Microsoft security alert is real

Posted on March 5, 2025 by Matt Longman
Microsoft security alert emails help you to know if someone is potentially trying to illegally access your Microsoft account. However, scammers and cybercriminals are well aware of this and have been known to use Microsoft security alert emails in an attempt to steal data from unsuspecting victims.
So how can you tell the difference between a real and a fake Microsoft security alert?
How to check if a Microsoft security alert is fake
1. Check the sender address
Microsoft support uses the following domains to send emails:
- accountprotection.microsoft.com
- microsoft.com
- microsoftsupport.com
- mail.support.microsoft.com
Microsoft is also starting to use the .microsoft domain across its sites, so you may start to see this soon across emails as well. Only Microsoft can use this, so it adds an extra layer of security for users and Microsoft account holders.
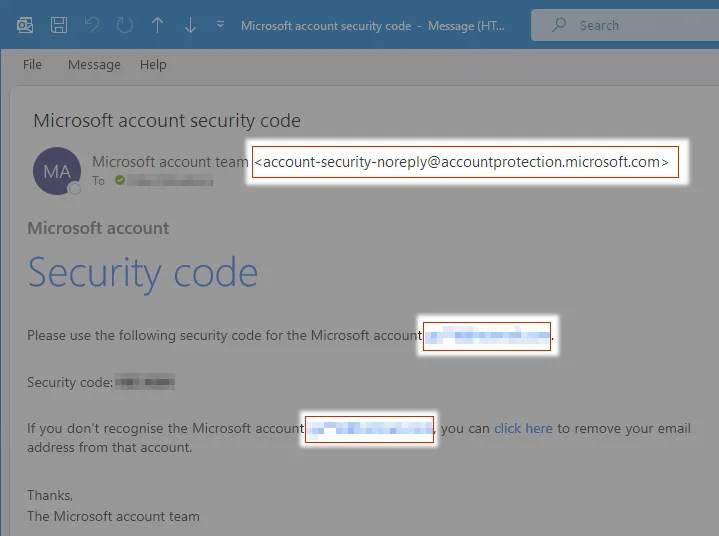
If the email you’ve received in your inbox isn’t from one of these email addresses, it could be a spam attempt.
2. Re-read the email
Scammers use a wide variety of tactics to try and get your information, and quickly. If the message contains threats or pressurising terms such as “Act now” or “Urgent action required”, it could be a phishing attempt.
Scammers often make mistakes with grammar and wording, making their messages look suspicious. Real alerts will give you clear instructions right away, not send you to click on multiple links.
3. Hover over the URLs
Be cautious with links in phishing emails, as they can lead to fake login pages or malicious websites. Before clicking, hover over the link to check the URL. Official Microsoft sites include:
- login.microsoftonline.com
- account.microsoft.com
- portal.office.com
- cloud.microsoft
If the URL looks suspicious or doesn’t match one of these trusted domains, do not click it, and report it as spam or to your IT team as a phishing attempt.
4. Be wary of attachments
Be on the lookout for suspicious attachments in emails claiming to be from Microsoft. Genuine security alerts from Microsoft will never include attachments. Scammers, on the other hand, often attach malicious files to their phishing emails, disguising them as photos showing where the account was logged into, security alert reports, or software updates. These attachments can be used to install malware or steal sensitive information from your device. To stay safe, never open attachments from unverified sources, even if they seem legitimate.
5. Look for impersonal language
Legitimate Microsoft security alerts usually contain personalised details that apply to you, such as:
- Your name
- The specific account or service affected
- Clear instructions on the actions you need to take
Phishing emails often use generic greetings like “Dear Customer” and have no references to any personal information. If a message feels impersonal or doesn’t address you by name when they would normally, it’s a good idea to be cautious.
How to cross-reference a security alert
If you have access to your account
If you still have access to your account, then you can verify the legitimacy of an alert. Log in directly to your Microsoft account and check for any recent notifications in the Security section, or unusual activity in the Recent Activity section. If you don’t see a matching alert, it’s likely to be a phishing attempt.
If you don’t have access to your account
If your account has been compromised, your IT team may be able to help. It’s always best to speak to them first to see what help they can offer you before attempting to contact Microsoft, as Microsoft may take longer to get back to you.
If you do need to contact Microsoft about a compromised account, head here.
What to do if you click on a phishing email
If you click on a phishing email, follow these steps:
- Do not provide any further information: Avoid responding to the email, filling out forms, or clicking on any links.
- Disconnect from the internet: Immediately disconnect from the internet to prevent any further potential harm.
- Run a virus scan: Update your antivirus software and run a full scan to detect and remove any malware.
- Change passwords: Change the passwords for all accounts that may have been compromised, including email, social media, and financial accounts.
- Notify your organisation: Inform your IT department or manager about the incident, so they can take necessary actions to protect the organisation’s systems and data.
Training is key to preventing phishing attacks
Highlighting scam techniques and awareness is essential and should be part of your regular cybersecurity training in your organisation. If you would like further advice or need to discuss what training options are available to you, please speak to your ramsac relationship manager or get in touch!







